Bitcoin, often referred to as digital gold, is a decentralized digital currency that has taken the financial world by storm. At the heart of this revolutionary system lies the enigmatic process of Bitcoin mining. In this blog, we will explore how Bitcoin mining works, the vital role of miners, and the fascinating rewards they earn for securing the network.
The Basics of Bitcoin Mining
At its core, Bitcoin mining is the process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain, the public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions. This process is essential for maintaining the integrity and security of the cryptocurrency network.
The Role of Miners
Miners are central players in the Bitcoin ecosystem. They are responsible for two primary functions:
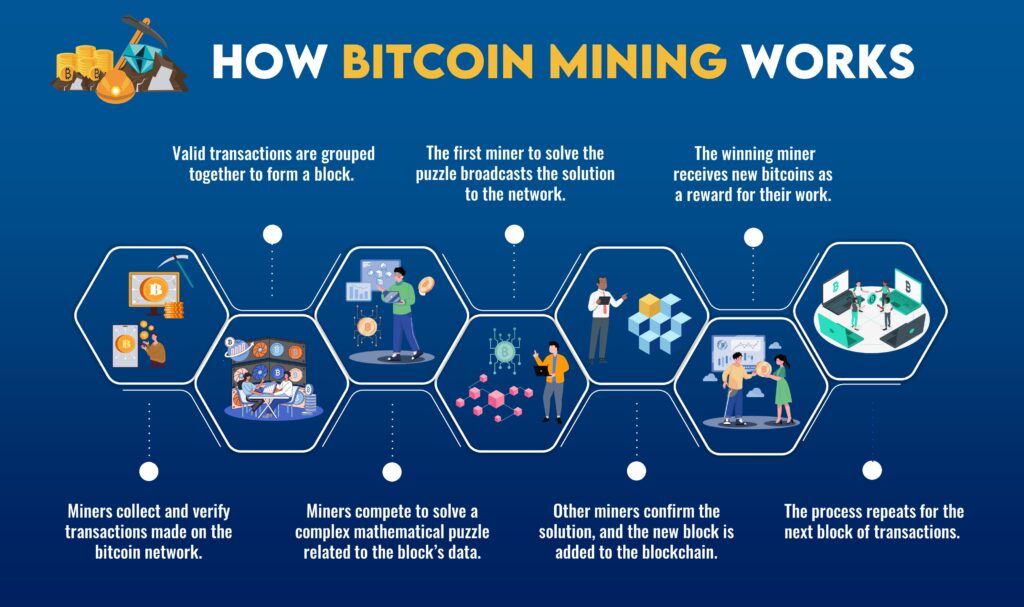
- Transaction Validation: Miners collect and validate a set of pending Bitcoin transactions, grouping them into a block. To ensure the transactions are legitimate and adhere to the network’s rules, miners verify that the sender has sufficient funds and that the transaction has not been spent before.
- Block Creation: Once a miner has successfully validated a set of transactions, they must create a new block. This involves solving a complex mathematical puzzle, often referred to as the “proof of work.” The first miner to solve this puzzle gets the opportunity to add their block to the blockchain.
The Proof of Work Puzzle
The “proof of work” puzzle is a critical component of Bitcoin mining. It is a cryptographic challenge that miners must solve to create a new block. The puzzle is based on a cryptographic hash function, which takes an input (the block’s transactions) and produces an output of a fixed length. Miners modify a value within the block, known as the “nonce,” to generate a hash that meets specific criteria. This process is resource-intensive and requires significant computational power.
Securing the Network
The proof of work puzzle serves two crucial purposes:
- Security: The difficulty of the puzzle makes it computationally expensive to create new blocks. This safeguards the network against malicious actors who might attempt to flood it with fraudulent transactions or attempt a “51% attack,” which would require controlling more than half of the network’s mining power.
- Consensus: The puzzle introduces a competitive element among miners. The first miner to solve it broadcasts their solution to the network. If other miners agree that the solution is valid, the new block is added to the blockchain. This consensus mechanism ensures that all nodes in the network maintain a consistent ledger.
Rewards for Miners
Bitcoin mining is not without its incentives. Miners invest substantial computational resources and energy into the process, and they are rewarded in two ways:
- Block Rewards: When a miner successfully creates a new block, they are rewarded with a fixed number of newly minted bitcoins. This is how new bitcoins are introduced into circulation. Initially, the reward was 50 bitcoins per block, but it undergoes a “halving” event approximately every four years, reducing the reward by half. As of the last halving in 2020, the block reward stands at 6.25 bitcoins.
- Transaction Fees: Miners also collect transaction fees from the transactions included in the blocks they mine. These fees are voluntarily paid by users to prioritize their transactions and incentivize miners to include them in the next block. Transaction fees vary depending on network demand and the urgency of the transaction.

ASIC Miners
(Application-Specific Integrated Circuits)
The Competitive Nature of Mining
Bitcoin mining is highly competitive. Miners from around the world invest in specialized hardware known as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) to maximize their computational power. The competition to solve the proof of work puzzle is fierce, as only one miner will successfully add a block to the blockchain. This competitive nature ensures the security and decentralization of the network.
The Environmental Impact of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining has faced criticism for its energy consumption. The computational power required to solve the proof of work puzzle is substantial, and many miners use electricity generated from non-renewable sources. However, it’s worth noting that the industry is continually evolving, and some miners are exploring greener options and renewable energy sources to mitigate the environmental impact.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is the backbone of the Bitcoin network. Miners play a crucial role in securing the system, validating transactions, and maintaining the blockchain’s integrity. In return for their efforts, miners are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees. The competitive nature of mining ensures the network’s security and decentralization. While Bitcoin mining has faced environmental concerns, it remains a fundamental and fascinating aspect of the cryptocurrency world, providing the foundation for a decentralized, digital economy.




