In a rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, interoperability is emerging as a crucial factor for the efficient and scalable functioning of these networks. Polkadot, with its innovative architecture, is leading the charge in enabling seamless interoperability among diverse blockchains. In this blog, we will introduce Polkadot as a multi-chain blockchain platform, explore the significance of interoperability, and delve into how Polkadot’s unique architecture allows multiple specialized blockchains, known as parachains, to connect and share information.
Introduction to Polkadot
Polkadot, often denoted as DOT, is a pioneering project designed to revolutionize the blockchain ecosystem. Founded by Dr. Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum, Polkadot aims to overcome the limitations of traditional blockchain networks by introducing an advanced multi-chain architecture.
At its core, Polkadot is built to enable interoperability, scalability, and security across different blockchains. It accomplishes this through a unique structure that facilitates the interaction of multiple blockchains, offering a cohesive and efficient network for decentralized applications (dApps) and services.
The Significance of Interoperability
Interoperability is the capability of different blockchain networks to communicate and work together seamlessly. It is essential for several reasons:
- Scalability: Interoperability enables various blockchains to process transactions concurrently, significantly increasing the network’s capacity and throughput.
- Efficiency: Transactions and data can be shared across different blockchains, reducing the burden on a single network and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Specialization: Different blockchains can focus on specific use cases or industries, catering to the diverse needs of developers and users.
- Cross-Chain Applications: It allows for the creation of cross-chain applications, where data and assets from one blockchain can be used on another.
- Security: Interoperability can enhance the security of the network by enabling the exchange of security-related information between blockchains.
Polkadot’s Architecture
Polkadot’s innovative architecture is the key to its interoperability and scalability. At its heart is a central relay chain, which coordinates and secures the network. Surrounding the relay chain are multiple specialized blockchains called parachains.
- Relay Chain: The relay chain is the core blockchain of the Polkadot network. It is responsible for ensuring security and coordination among all parachains. The relay chain validates transactions and finalizes the overall state of the Polkadot network.
- Parachains: Parachains are individual blockchains that connect to the relay chain. These parachains can be customized to serve specific purposes or industries. For instance, one parachain may be designed for finance, while another could cater to supply chain management. By creating specialized blockchains, Polkadot enables developers to focus on their unique use cases without compromising the overall network’s efficiency.
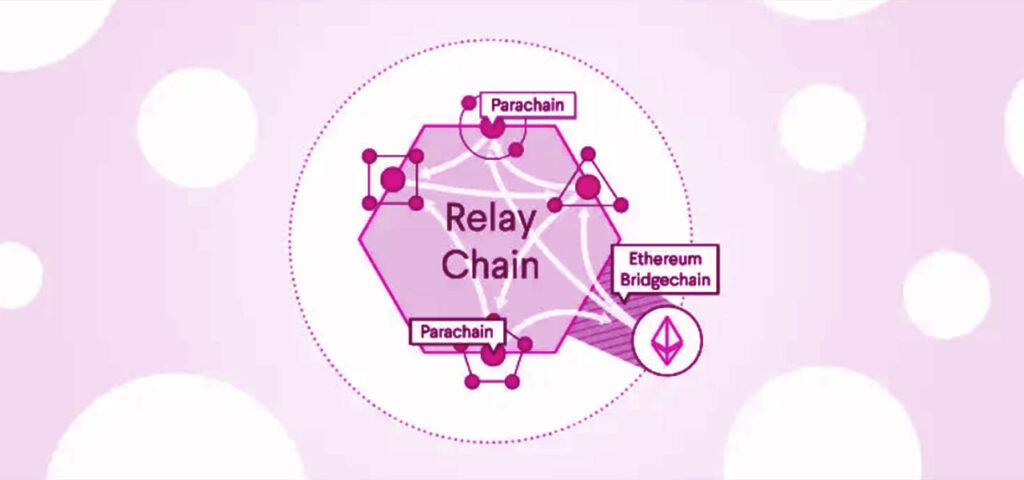
Bridges and Cross-Chain Communication
Polkadot’s approach to interoperability doesn’t stop at just connecting parachains. It also offers bridges to external blockchains, allowing them to communicate and share data with the Polkadot network. These bridges play a critical role in expanding Polkadot’s reach and ensuring seamless interaction with other blockchain ecosystems.
One example of such a bridge is the Bitcoin bridge, which connects the Polkadot network to the Bitcoin blockchain. This bridge enables the transfer of assets between the two networks, making it possible to utilize Bitcoin within the Polkadot ecosystem.
Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) Consensus
Polkadot employs a consensus mechanism called Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) to secure its network. In NPoS, DOT holders nominate validators to participate in the consensus process. These validators propose and validate new blocks on the network, ensuring its security and reliability.
The innovative aspect of NPoS is its ability to dynamically adapt to changing network conditions. Validators can be replaced if they misbehave or fail to fulfill their responsibilities, maintaining the network’s integrity.
Use Cases and Applications
The versatility and interoperability of Polkadot open the doors to a wide range of use cases and applications. Some of the most promising areas include:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Polkadot’s interoperability allows DeFi projects to operate seamlessly across multiple blockchains, leveraging the benefits of various ecosystems.
- IoT and Supply Chain Management: The network’s specialization enables efficient data sharing and traceability, making it an ideal platform for IoT and supply chain solutions.
- Cross-Chain Applications: Polkadot’s unique architecture is particularly appealing to developers creating cross-chain applications, enabling the transfer of assets and data between different blockchains.
- Custom Blockchains: Enterprises can develop customized blockchains tailored to their specific needs, offering a highly flexible and efficient solution.
Conclusion
Polkadot stands as a beacon of innovation in the blockchain space, offering an interoperable and scalable network for a diverse range of applications. With its multi-chain architecture and parachains, Polkadot addresses the limitations of traditional blockchains while providing the foundation for a secure, efficient, and versatile decentralized ecosystem. As the blockchain and cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, Polkadot’s commitment to interoperability and specialization positions it as a vital player in the future of blockchain technology.




